What is ARP?
- ARP is known as the Address resolution protocol. It works between the network layer and the data link layer.
- There is also a reverse protocol known as RARP which finds IP address from MAC address and IP is found from the DNS.
- There is an ARP table where there is ARP and MAC addresses exist. Every router and host has this.
- ARP finds the MAC (Media Access Control) address also known as the hardware address of a host from its known IP address
- Each IP node which can be a host or a router on a LAN (Local Area Network) has an ARP table.
- It is used when an IP protocol is used over the Ethernet.
- It is a request-reply protocol which means the request and response work simultaneously. Request messages are used to request the MAC address while the ARP reply message is used to send the requested MAC address
Network layer has many protocols like
- ICMP
- IGMP
- IP
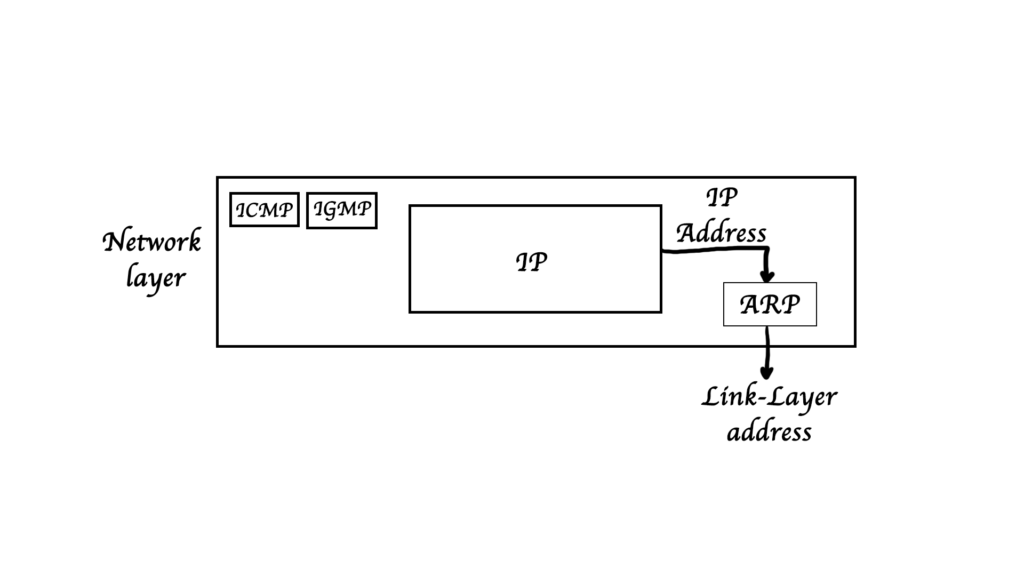
- ARP is not encapsulated in an IP packet but it is embedded in the ethernet frame.
- ARP has a different packet and it sits in the payload section
- IP datagram is in ARP
ARP Working
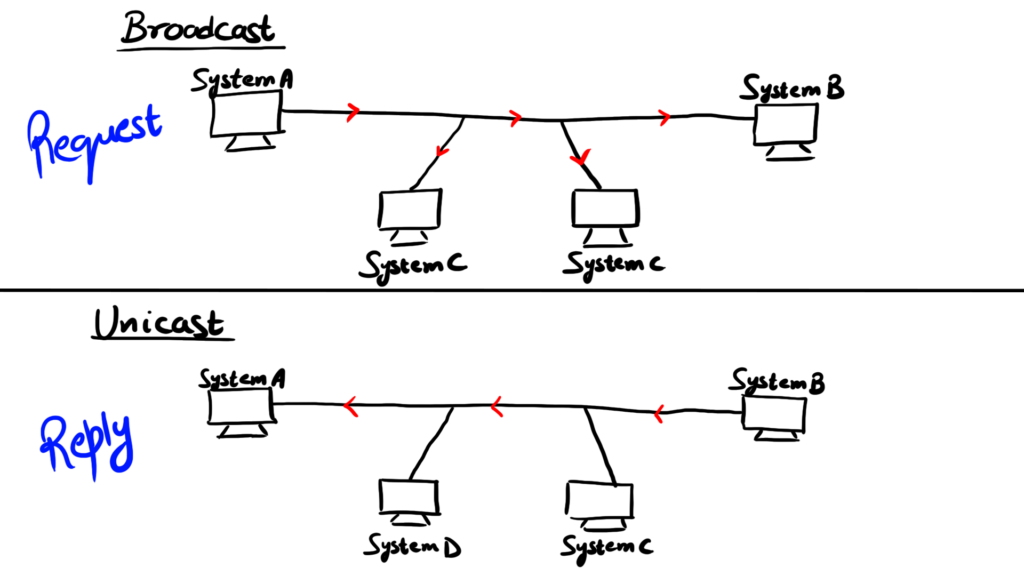
- As we do not know the MAC of System B so the question now arises how will we send the request to System B to know its MAC Address?
- But here System A knows the IP of System B so it will send the ARP request through the IP address of System B
- The request is sent as looking for link-layer address of a node with IP address N2 and it will be broadcasted to all the nodes
- All nodes will receive the ARP packet and then will check the IP address if it matches with their IP if it does not matches the packet is discarded and if it matches then it will reply and send MAC and will do a unicast
- The reply is in form of "I am at the node and my link-layer address is xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx.
ARP Format
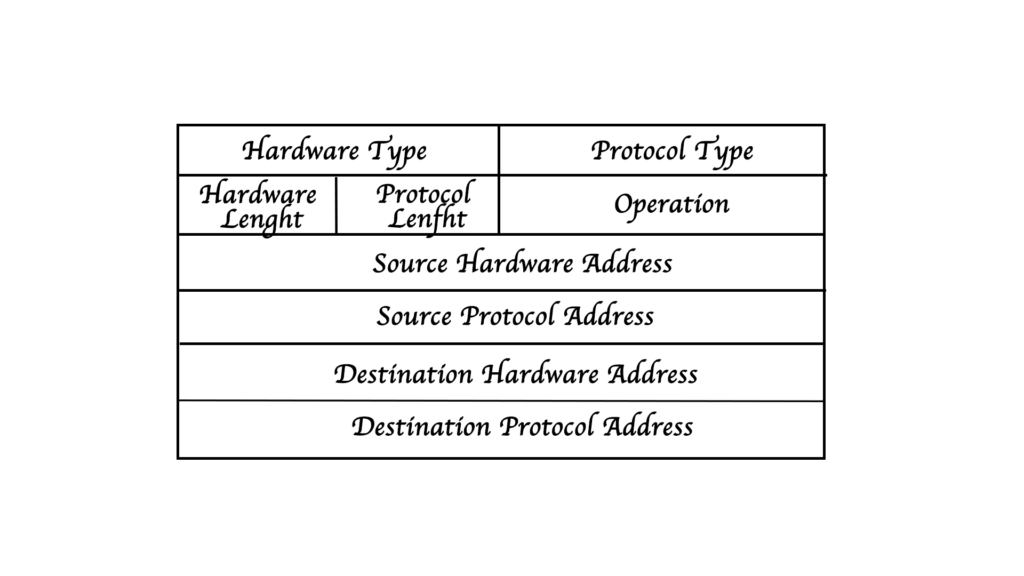
The above diagram shows how a ARP format looks and below I have explained all the terms :
- Hardware Type: It is of 16-bits and stores the hardware protocol used
- Protocol Type: The protocol which is used such as IPv4 or IPv6
- Hardware Lenght: Stores the MAC address lenght i.e 6 bytes
- Protocol Lenght: Stores the IP address lenght i.e 4 bytes
- Opertation: 1 is for request and 2 is for reply
- Source Hardware Address: Link layer address of the source
- Source Protocol Address: IP address of the source
- Destination Hardware/MAC address: Empty in case of request i.e 0 and filled with MAC in case of reply
- Destination Protocol Address: It stores the IP of the destination
The last four fields i.e 6, 7, 8 and 9 are very important for the ARP format.
ARP Cache
After the MAC address is found in the reply the ARP sends it to the source where it stores table for future reference.
Every time first cache is seen and if the MAC is not found then only the ARP will send again.
There is also a timeout period for this also
The further communications can use the MAC address form the table
ARP Cache Timeout
It indicates the time for which the MAC address in the ARP cache can reside
Also do not let your curiosity fade away and increase your knowledge and skills on networking and ethical hacking on Hackers Paradise. Click below to learn more:
Above I have covered all the important information regarding the ARP but if you want to dive deeper into the topic you can refer to the Wikipedia article below :
