What is a MAC address?
The word MAC Address stands for Media Access Control Address. Also called physical address or hardware address
It is one of the most important parts of the Data Link Layer
It does a node-to-node delivery and it helps us to communicate or transfer data from one computer to other
It works between the nodes between the source to the destination.
It is a unique 48-bit hardware number which is embedded by the manufacturer into the network card which is known as Network Interface Card
This MAC address cannot be changed as it is embedded permanently into the device when it was manufactured.
It is unique worldwide i.e no two devices as such can have the same MAC address in the same link and is unique for the nodes like the PC, Laptop etc.
Format of MAC address
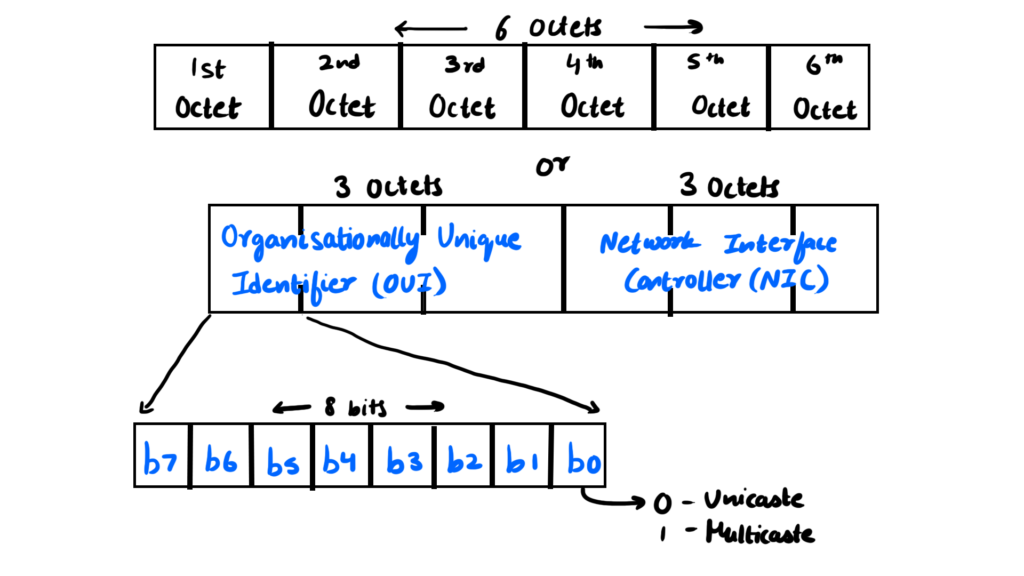
- It is a 12-digit hexadecimal number (6-Byte binary number)
- The first 6 digits of the MAC address identify the manufacturer which is called an Organisational Unique Identifier (OUI) which is assigned by IEEE
- This can be common for many devices as many devices can be made by same company
- Example
- MAC address - 00:11:22:33:44:55
- OUI - 00:22:22
- The last 6 digits of the MAC address represent the Network Interface Controller, which is assigned by the manufacturer itself.
- This will be unique for everyone
- Example
- MAC address - 00:11:22:33:44:55
- Network Interface Controller - 33:44:55
Types of Link-Layer Address
- Unicast - B2:25:44:21:88:D8
- It like the same conventional MAC address
- First byte’s least significant digit should be zero
- 2 - 0010
- Last is 0 therefore unicast
- Multicast - B7:25:44:21:88:D8
- First byte’s least significant digit should be one
- 7 - 0111
- Broadcast - FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF
- Sends to all
- All the bits are set
Octet
The two digit pair between a colon is an octate.
- Example
- MAC Address - 00:11:22:33:44:55
- Octate - 00, 11, 22, 33, 44 and 55
Working of MAC Address
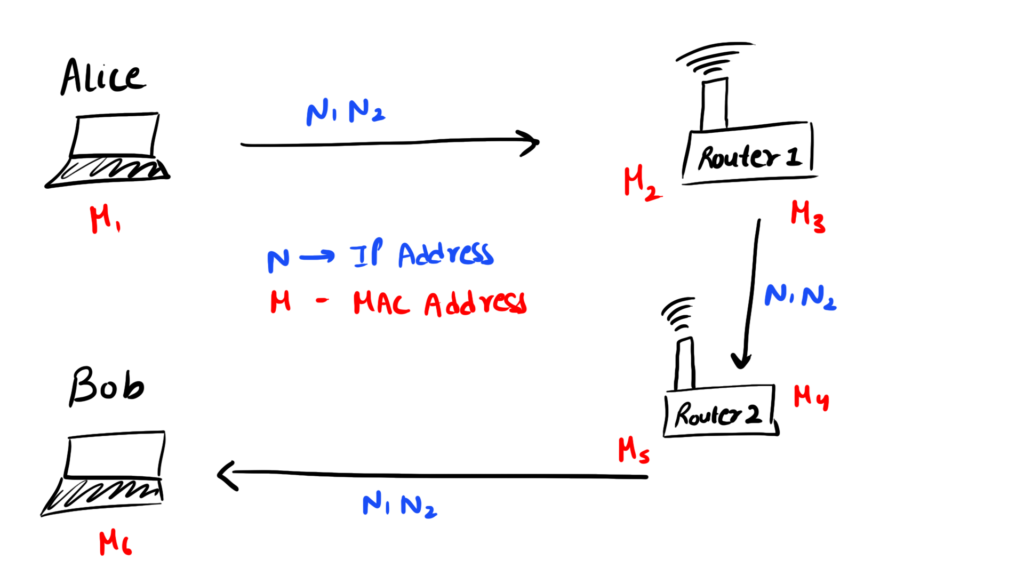
- Alice wants to send some information to Bob
- We have to send frame from Alice to Bob
- First Alice should know Bob IP address which she can get from the DNS
- Source IP is of Alice and destination of IP should be of Bob
- Now we should know MAC of Router 1 as it is connected to Alice which is M2
- Router 1 has 2 links M2 and M3
- Alice transfer to Router 1 through M2 as destination MAC and then Router 1 checks and finds that it has to send data forward now because the Destination IP is not of Router 1
- Now Router 1 will put the source address as its address (M3) and the destination address of Router 2 which is M4
- Router 2 sees destination IP is not of Router 2 so it will send it forward to Bob as it knows Bob's MAC address
- In full journey IP’s does not change but the source and destination MAC address changes
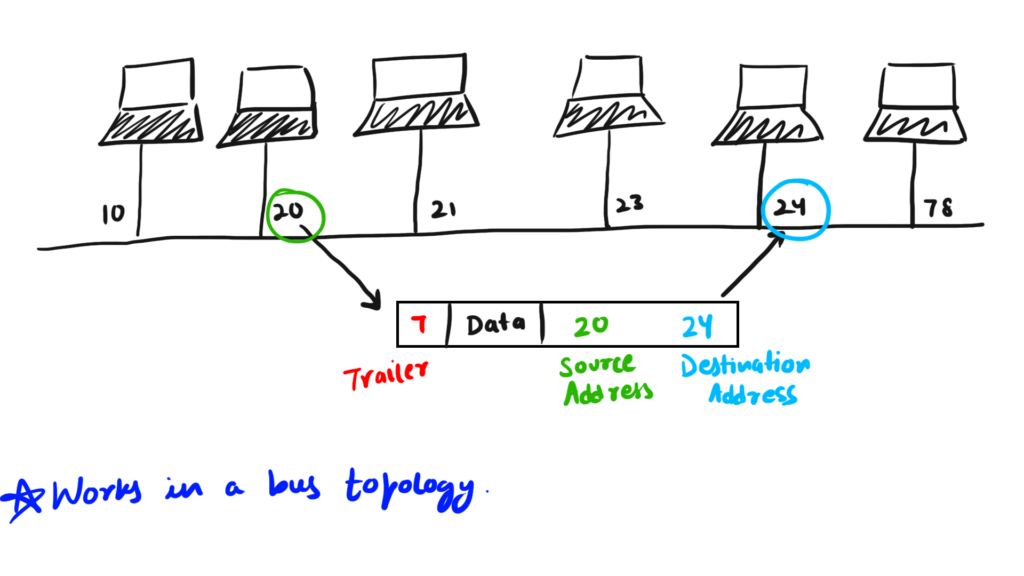
Above a shared medium, which is a bus topology, is an old medium and is not used nowadays. In this, as all the computers are on the same link or the network node 20 can directly share information with node 24.
