VLSM
VLSM stands for Variable Length Subnet Mask where a subnet design uses more than one mask for different subnets for single class A, B, C or a network
It is also called subnetting of a subnet
In FLSM (Fixed Length Subnet Mask) all the subnets have equal size but in VLSM, the subnet's size is variable and can also have a variable number of hosts.
This also helps to reduce the wastage of IP addresses.
To understand VLSM in a better way let us take an example
If our requirement for the network is something like this 👇
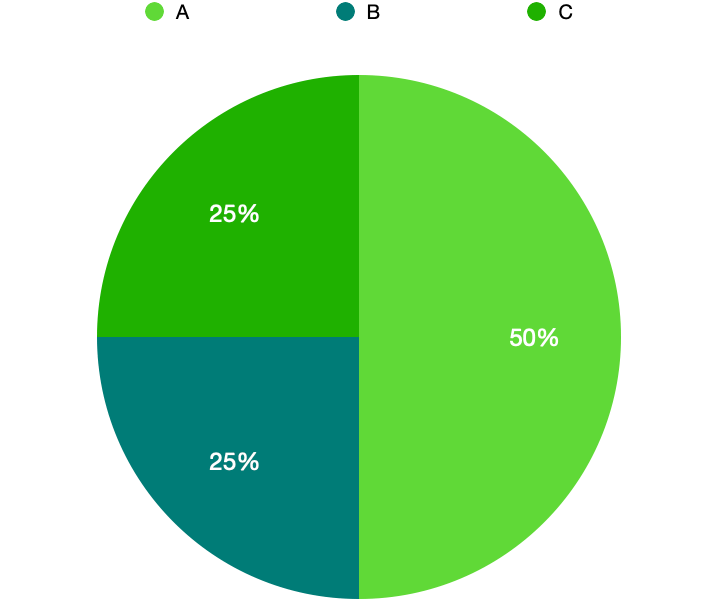
We want to allocate 300.2.1.0. to three different networks
- We need 120 (50%) addresses for the network A
- We need 60 (25%) addresses for the network B
- We need 60 (25%) addresses for the network C
Now if we use FLSM (Fixed Length Subnet Mask), we have to assign 128 bits and 8 bytes would be left but for network B and network C we will have no other option but to assign 128 bits and it is fixed. This would have resulted in the wastage of a large number of IP Addresses.
Now we have to find a way to reduce the wastage of IP addresses and that way is to use VLSM (Variable Length Subnet Mask)
- Address - 300.2.1.0
- Binary - 100101100.00000010.00000001.00000000
- Net ID - 24 bits
- Mask - 255.255.255.0
- For network A - 300.2.1.0
- Binary - 100101100.00000010.00000001.00000000
- Net ID - 25 bits
- Mask - 255.255.255.128
- For network B - 300.2.1.0
- We will allow 6 bits as the number of possible hosts will be 26 which is 64 -2 = 62 hosts
- Binary - 100101100.00000010.00000001.10000000
- Net ID - 26 bits
- Mask - 255.255.255.192
- For network C - 300.2.1.0
- We will allow 6 bits as the number of possible hosts will be 26 which is 64 -2 = 62 hosts
- But to avoid ambiguity with the network B address we will make 7th bit from last as 1
- Binary - 100101100.00000010.00000001.11000000
- Net ID - 26 bits
- Mask - 255.255.255.128
Now if you are preparing for some kind of exam then you might want to learn about converting a decimal IP address to binary. But if not then you can use the converter and save yourself from the hassle.
Do not forget to comment on any doubts related to the topic and we will solve your doubt as soon as possible. Also, comment on your feedback related to the content.
Also do not let your curiosity fade away and increase your knowledge and skills on ethical hacking and networking only on Hackers Paradise. Click below to learn more :
